|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
Overview
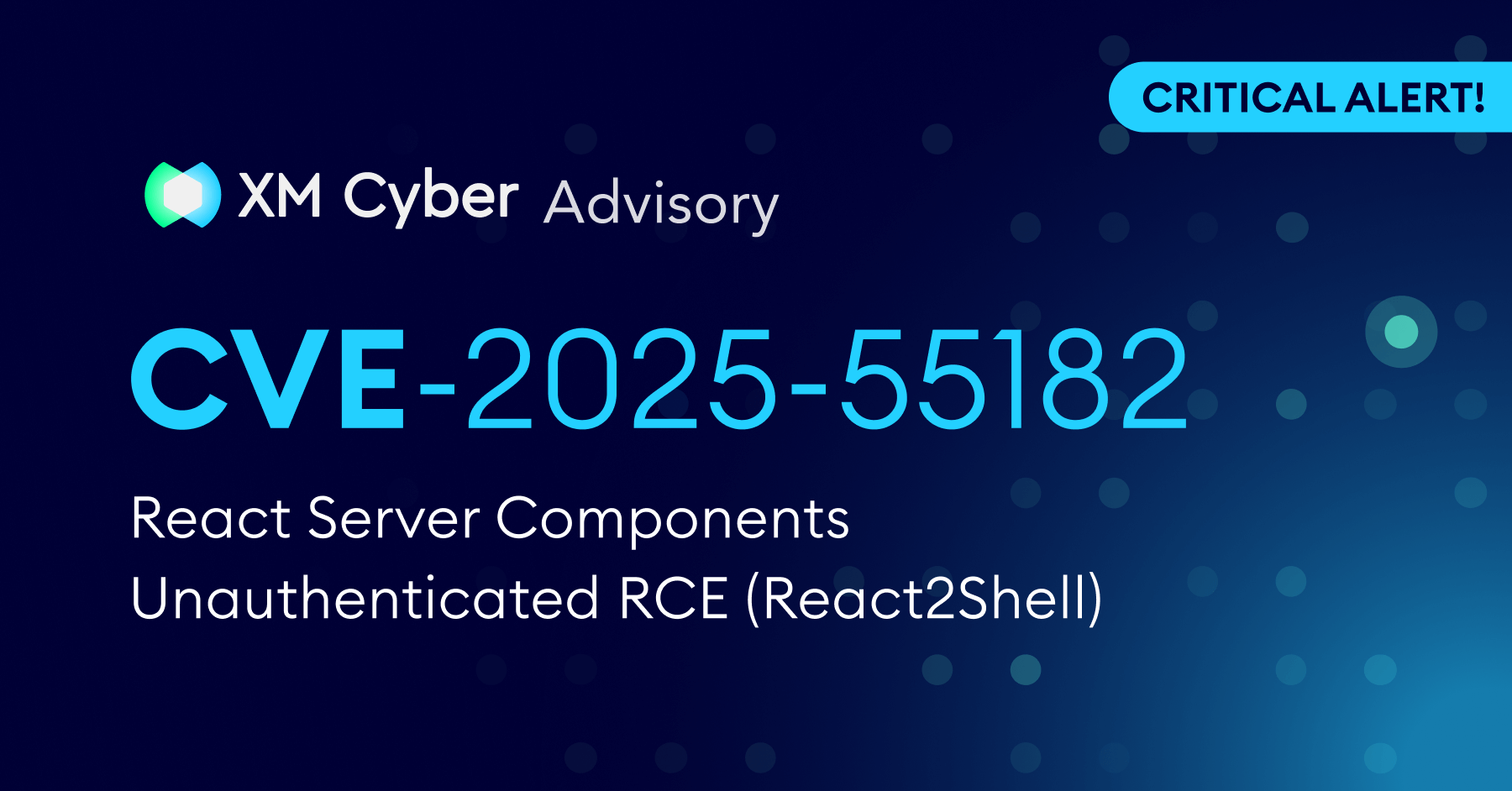
On December 3, 2025, the security community was alerted to a critical vulnerability in the React Server Components (RSC) ecosystem, now widely referred to as React2Shell. Tracked as CVE-2025-55182, this flaw has been assigned the maximum severity score of CVSS 10.0 and allows for unauthenticated Remote Code Execution (RCE).
The Threat
Given the widespread adoption of React and frameworks built on it, like Next.js, this is a top-priority security incident for organizations globally and requires immediate patching. The exploit of this vulnerability is unauthenticated and remote, requiring only a specially crafted HTTP request to achieve full remote code execution. The vulnerability exists in the default configuration of affected applications, meaning standard deployments are immediately exploitable without any misconfigurations. According to the React team, even if your app does not implement any React Server Function endpoints it may still be vulnerable if your app supports React Server Components.
- CVSS Score: 10.0 (Critical).
- Affected Versions: React versions 19.0, 19.1.0, 19.1.1, and 19.2.0, as well as frameworks that implement RSC, most notably Next.js versions 14.3.0-canary through 16.x.
- Active Exploitation: AWS reported that its threat intelligence teams started seeing exploitation attempts by China-linked threat actors within hours of public disclosure.
- Attack Surface: React is an open source JavaScript library designed for creating application user interfaces, which powers millions of websites. According to Wiz data, 39% of cloud environments contain vulnerable React instances.
Exploitation Within Hours
Based on immediate threat intelligence reports, exploitation attempts began within hours of the public disclosure, primarily attributed to sophisticated, state-linked actors. The attack groups publicly linked to exploiting or actively testing the React2Shell vulnerability are China state-nexus threat groups Earth Lamia and Jackpot Panda.
Earth Lamia is a China-nexus cyber threat actor known for exploiting web application vulnerabilities to target organizations across Latin America, the Middle East, and Southeast Asia. The group has historically targeted sectors across financial services, logistics, retail, IT companies, universities, and government organizations.
Jackpot Panda is a China-nexus cyber threat actor primarily targeting entities in East and Southeast Asia. The activity likely aligns to collection priorities pertaining to domestic security and corruption concerns.
Immediate Recommendations
React issued official mitigation guidance to update React and Next.js to the latest patched versions:
- Users of React are urged to update to versions 19.0.1, 19.1.2, or 19.2.1.
- Next.js users should upgrade to versions 15.0.5, 15.1.9, 15.2.6, 15.3.6, 15.4.8, 15.5.7, or 16.0.7.
- Users of other RSC-enabled frameworks (RedwoodJS, Waku, React Router, etc.) are advised to check official channels for updates and patches.
In addition to that there are mitigations and best practices that organizations need to adopt in order to protect from React2Shell and similar vulnerabilities:
- Deploy WAF rules: Implement WAF rules to block exploitation attempts. Google Cloud users can use the cve-canary preconfigured rule with specific match conditions for next-action and rsc-action-id headers. Other WAF providers likely have similar signatures available.
- Verify deployments: Redeploy all affected services (Cloud Run, GKE, App Engine, etc.) after updating dependencies to ensure the patched code is running.
- Continuous detection: Actively monitor your external attack surface to identify any overlooked or shadow instances of React/Next.js applications that remain vulnerable. Continuous scanning helps ensure no asset is left unprotected.
How XM Cyber Can Help with CVE-2025-55182
The criticality of React2Shell and the instant exploits by threat groups are sending security teams on a frantic attempt to patch all instances before they are attacked. These efforts remind the more veteran security leaders of the good old days, when Log4J sent them on a similar quest. This is exactly the purpose of Continuous Exposure Management – to identify which instances specifically compromise your business and get ahead of attackers by fixing those first. XM Cyber helps organizations diffuse the fire drills these critical vulnerabilities create by mapping how attackers can deploy them in your environment, using a digital twin approach, and proving which ones should be fixed first. This empowers teams to focus efforts on fixing what actually has an impact on their business rather than wasting time investigating critical vulnerabilities that are less relevant to their specific environment.
XM Cyber’s External Attack Surface Management (XM EASM) enables discovering all external-facing instances which are vulnerable to this risk. Utilizing continuous monitoring, automated scanning, and autonomous pen testing, XM Cyber EASM discovers, validates and alerts vulnerable instances of React/Next.js applications. If any are detected, the platform uniquely maps the end-to-end attack path from the external-facing instances to the internal network in order to validate reachability and exploitability on the attack graph, highlight which instances compromise critical assets and must be fixed first, and provides step-by-step guidance on how to address them.
The XM Cyber unique Attack Graph Analysis™ enables customers to clearly understand how vulnerabilities, along with other exposures such as misconfigurations and identity issues, can be combined by attackers to compromise their critical assets. It also allows proactive, prioritized action along attack paths that are exploitable in your environment, focusing on rapid remediation of choke points, where multiple paths converge before compromising critical assets.
If you’re ready to get off the treadmill and start focusing on remediation that prevents breaches, contact us and we’ll show you how it works.