|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
Exposure Management is a proactive approach to cybersecurity that involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential vulnerabilities. By understanding and reducing an organization’s attack surface, Exposure Management helps prevent cyberattacks and minimizes their impact. In this article, we’ll take a deep dive into what Exposure Management is, why it’s essential, how it ties into CTEM, and how to best implement it in your organization.
To Start, What is Exposure Management?
Exposure Management is the systematic process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating security risks that an organization faces. Exposure Management seeks to understand all the possible ways in which an organization’s systems, networks, and data could be vulnerable to threats – and take proactive steps to reduce this risk.
The Exposure Management process begins by identifying organizational assets that could be targeted – servers, databases, applications, devices, personnel and more. Once these assets have been identified, the next step in the process is to assess the level of exposure of each asset to potential threats. This is accomplished by evaluating how easily each asset could be accessed or compromised – taking into account factors like outdated software, weak passwords and other credential-based issues, misconfigurations, unpatched vulnerabilities, and more.
Then, organizations prioritize the exposures they identified based on their potential impact. High-priority exposures will, of course, be addressed first – via technical measures (patching, upgrading, refreshing security protocols, etc.) and policy changes (enforcing stronger password requirements, limiting access to sensitive data, and more).
Effective Exposure Management is an iterative process. Thus, continuous monitoring and reassessment is key to its success. As the threat landscape evolves and new vulnerabilities emerge, organizations need to regularly update their Exposure Management strategies to ensure ongoing protection.
Why do Organizations Need an Exposure Management Strategy?
Exposure Management empowers organizations to take the initiative in defending themselves against cyber threats by systematically reducing their exposure and pre-empting potential attacks. A crucial part of any organization’s cybersecurity strategy, Exposure Management matters because it grants:
- A Comprehensive Perspective – Exposure Management provides organizations with a comprehensive view of their attack surface. By identifying vulnerable areas within their IT systems, organizations can better understand their risk landscape and take targeted actions to secure critical assets.
- A Proactive Approach – Exposure Management focuses on prevention, emphasizing proactive measures.
- Increased Connectivity – Organizations are more connected and interconnected than ever before. The rise of Internet of Things (IoT), work from home (WFH) and Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) – to name a few trends – has massively expanded the number of endpoints. Exposure Management helps address these complexities.
- Optimal Prioritization – Exposure Management allows organizations to prioritize their responses effectively. By assessing not just vulnerabilities but exposures, they can better allocate limited resources to address high-risk areas faster.
- Operational Resilience – Integrating Exposure Management strengthens an organization’s overall operational resilience. It ensures robust protection, compliance, and the ability to withstand cyber threats more effectively.
Top 5 Exposure Management Techniques
Exposure Management is critical for safeguarding digital assets. By implementing these five Exposure Management techniques, organizations can significantly reduce their risk of cyberattacks and protect their valuable assets:
- Attack Surface Management (ASM)
Attack Surface Management identifies, prioritizes, and secures all potential attacker entry points in an organization’s systems and networks. This includes external-facing assets like websites, applications, and network devices, as well as internal systems, cloud environments, devices, IoT devices and more. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of the attack surface, organizations can focus their resources on the most critical vulnerabilities and implement appropriate safeguards.
- Vulnerability Management
This technique identifies, assesses, and mitigates software and system vulnerabilities. Vulnerability Management tools regularly scan systems and applications for weaknesses, prioritize them based on severity and potential impact, and implement patches or other countermeasures. Effective Vulnerability Management requires a combination of automated scanning tools, manual assessments, and a robust patch management process.
- Threat Intelligence
Threat intelligence is the process of collecting, analyzing, and disseminating information about potential threats to an organization. This includes information about adversaries, their tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs), as well as emerging threats and vulnerabilities. By understanding the threat landscape, organizations can proactively implement defenses, detect attacks earlier, and respond more effectively to incidents.
- Incident Response Planning
An incident response plan outlines the steps an organization will take in the event of a security breach. It covers various aspects of incident management, including detection, containment, eradication, recovery, and lessons learned. A well-defined and tested incident response plan can minimize the impact of a security breach and ensure a swift and coordinated response.
- Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
Exposure Management is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and evaluation. To this end, organizations should regularly assess the effectiveness of their security controls, identify new threats and vulnerabilities, and make necessary adjustments to their security posture. This includes monitoring network traffic, system logs, and security alerts, conducting vulnerability assessments, and staying informed about the latest security trends.
The Benefits of Exposure Management
Exposure Management is a proactive and strategic approach that significantly enhances an organization’s security posture. By shifting focus from reactive threat management to proactively identifying and addressing exposures, organizations gain numerous benefits:
- A Holistic Perspective – Exposure Management offers a comprehensive view of an organization’s digital attack surface. This enables not only a better understanding of risk, but also the development of targeted and efficient security strategies. By systematically identifying vulnerabilities before adversaries can exploit them, organizations can address potential weaknesses proactively, reducing the likelihood of successful attacks.
- Better Adaptability – Exposure Management fosters adaptability in a dynamic threat landscape. It empowers organizations to respond swiftly to emerging threats by prioritizing responses based on the most severe risk to the business. This ensures more efficient allocation of scarce resources to prevent attacks and minimizes the impact of attacks when they do occur.
- Reduced Risk – Exposure Management significantly decreases the risk of cyberattacks. With greater visibility into the entire attack surface, organizations can detect and remediate vulnerabilities more efficiently. This proactive stance not only prevents breaches but also helps mitigate potential financial losses, reputational damage, and operational disruptions.
- Cost Savings – Exposure Management delivers substantial cost savings. Preventing cyberattacks is far more economical than paying for their aftermath. (Check out this blog on how to get your CFO on board with your initiatives here.) By closing security gaps before they are exploited, organizations can avoid the hefty expenses associated with incident response, recovery, and potential legal liabilities. Additionally, a strong security posture may lead to reduced cyber insurance premiums.
What’s the Connection Between CTEM and Exposure Management?
Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) and Exposure Management are closely related concepts, but they operate on different levels.
CTEM is a structured process designed to assess, prioritize, and manage an organization’s exposure to cyber threats. It involves multiple stages, including discovering assets, identifying vulnerabilities, assessing the potential impact of these vulnerabilities, and remediating them in a prioritized manner. CTEM is a continuous, evolving approach that seeks to align security measures with the dynamic nature of cyber threats and organizational changes.
Exposure Management, on the other hand, refers to the specific function within the CTEM process that focuses on understanding and reducing the organization’s exposure to cyber risks. It involves identifying weak points in the organization’s systems and network, evaluating the potential for exploitation, and implementing measures to minimize these risks. Exposure Management is a key activity within the broader CTEM framework, aimed at translating threat intelligence into actionable remediation steps.
So CTEM and Exposure Management are connected because CTEM provides the overarching structure for managing cyber risks, and Exposure Management is a core function within this process, helping organizations actively minimize their risk exposure as part of their CTEM strategy.
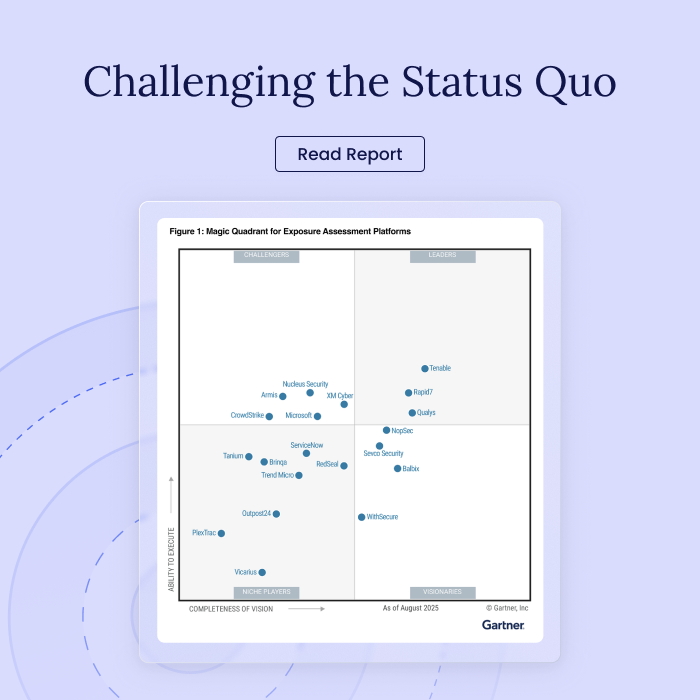
(Sidenote: At XM Cyber, we’ve been doing CTEM since before it was called CTEM. And as mentioned above, CTEM in itself, isn’t a solution – it’s a framework. The holistic approach of XM Cyber’s Continuous Exposure Management solution enables organizations to optimally implement Exposure Management, by identifying and remediating potentially problematic areas before attackers can exploit them.)
Conclusion
With a strategic approach to Exposure Management, organizations can reduce risk and improve security posture over time. Yes, it’s a nuanced process that takes time and resources to implement and get it right. But it’s an essential element to making a true impact in your defense against expanding and changing threats.